Medical robot technology is a new interdisciplinary research field, which integrates medicine, robotics, artificial intelligence, biomechanics, materials science, computer graphics and images, and has become a research hotspot in the international robot field.
Since 1985, after the researchers completed the neurosurgery of robot-assisted positioning with the help of PUMA560 industrial robot, advanced robot technology has been widely used in surgery, image positioning, rehabilitation training, nursing service, consultation, medical teaching, hospital logistics and other fields, involving clinical departments including orthopedics, neurosurgery, cardiovascular, thoracic surgery, hepatobiliary surgery, craniofacial surgery, urology and so on.

This not only promoted the revolution of traditional medicine, but also promoted the development of new technologies and theories. At present, according to the different functions of medical robots, they can be divided into four categories: surgical robots, rehabilitation robots, non-surgical diagnosis and treatment robots and service robots. Different categories of medical robots include different sub-categories, such as neurosurgical robots, orthopedic surgical robots, vascular intervention robots, intelligent prostheses, exoskeleton robots and assisted rehabilitation robots.
According to the statistics of Boston Consulting Group, surgical robots are the most frequently used products among medical robots, with a market share of about 60%, followed by rehabilitation robots such as exoskeletons and intelligent prostheses. While non-surgical diagnosis and treatment robots and service robots account for a relatively small proportion.
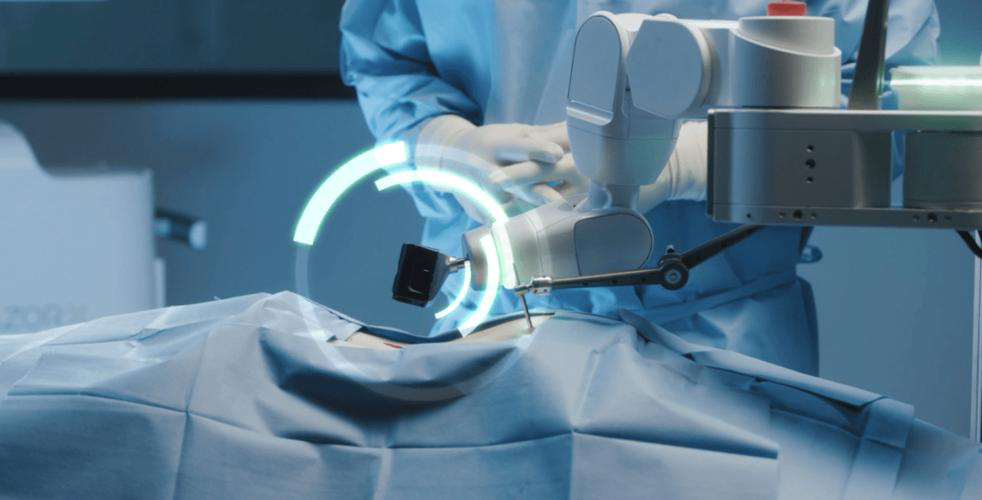
The first type of robots in medical treatment is the surgical robot. The number of medical robot operations increased from 25,000 in 2005 to 650,000 in 2016. 80% of prostatectomy is done by robots. Surgical robot is a combined device of a group of devices. It is usually composed of an endoscope (probe), surgical instruments such as knives and scissors, miniature cameras and joysticks. According to foreign manufacturers, the working principle of surgical robots in use at the current stage is to perform surgery through wireless operation. That is, doctors sit in front of the computer display screen, carefully observe the lesions in patients through the display screen and endoscope, and then accurately remove (or repair) the lesions through the scalpel in the hands of robots.
Robot’s most obvious characteristic is that it has the dexterity which the human does not have, its foundation lies in: 1) The tremor filter system can filter out the surgeon’s hand tremor; 2) The motion reduction system can reduce the surgeon’s motion range proportionally (5: 1). At present, surgical robots are widely used in bone surgery, neurosurgery, speculum surgery and interventional therapy.
Types of robot surgery: partial gastrectomy, appendectomy, gastrostomy, mastectomy, etc. in general surgery; cholecystectomy, hilar jejunostomy, choledostomy, etc. in hepatobiliary surgery; hysterectomy, ovarian dislocation, hysteromyoma resection in obstetrics and gynecology; urology, prostatectomy, nephrectomy, ureteroplasty, etc.; thoracic and cardiac surgery, such as beating heart bypass, valve repair, esophageal tumor resection, etc.
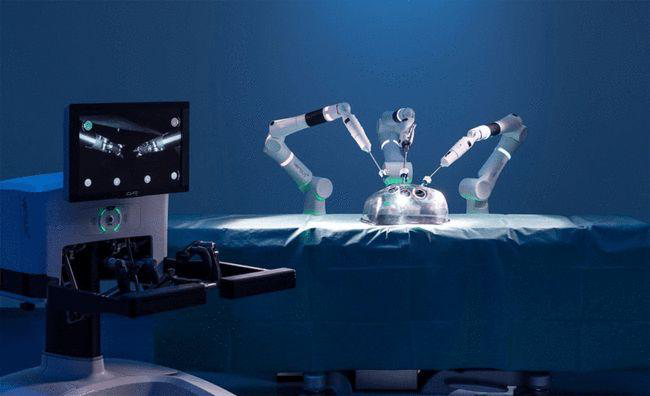
There are also other three types of robots in medical treatment, which will be introduced in the next section. With more research and development in the field of medical treatment, the efficiency and precision of it can be highly improved.



